New NASA Earth System Observatory to Help Address, Mitigate Climate Change
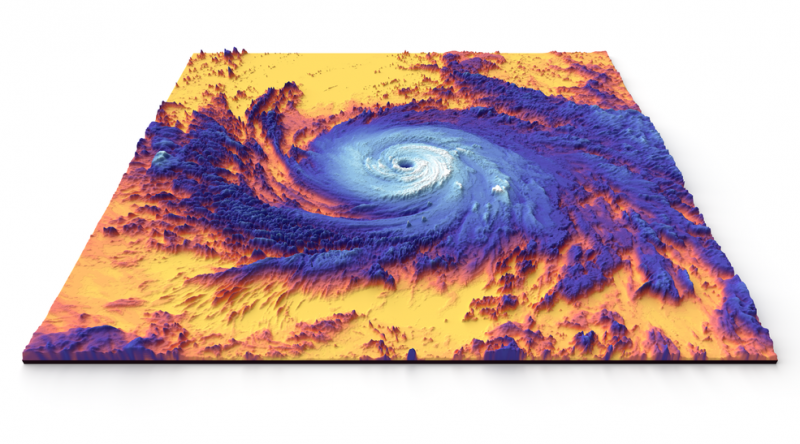
NASA’s new Earth System Observatory will guide efforts related to climate change, disaster mitigation, fighting forest fires, and improving real-time agricultural processes – including helping to better understand Category 4 to 5 hurricanes such as Hurricane Maria, shown here in a 2017 thermal image captured by NASA’s Terra satellite.
With the Earth System Observatory, each satellite will be uniquely designed to complement the others, working in tandem to create a 3D, holistic view of Earth, from bedrock to atmosphere.
“I’ve seen firsthand the impact of hurricanes made more intense and destructive by climate change, like Maria and Irma. The Biden-Harris Administration’s response to climate change matches the magnitude of the threat: a whole of government, all hands-on-deck approach to meet this moment,” said NASA Administrator Sen. Bill Nelson. “Over the past three decades, much of what we’ve learned about the Earth’s changing climate is built on NASA satellite observations and research. NASA’s new Earth System Observatory will expand that work, providing the world with an unprecedented understanding of our Earth’s climate system, arming us with next-generation data critical to mitigating climate change, and protecting our communities in the face of natural disasters.”
The observatory follows recommendations from the 2017 Earth Science Decadal Survey by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine, which lays out ambitious but critically necessary research and observation guidance.
Areas of focus for the observatory include:
- Aerosols: Answering the critical question of how aerosols affect the global energy balance, a key source of uncertainty in predicting climate change.
- Cloud, Convection, and Precipitation: Tackling the largest sources of uncertainty in future projections of climate change, air quality forecasting, and prediction of severe weather.
- Mass Change: Providing drought assessment and forecasting, associated planning for water use for agriculture, as well as supporting natural hazard response.
Surface Biology and Geology: Understanding climate changes that impact food and agriculture, habitation, and natural resources, by answering open questions about the fluxes of carbon, water, nutrients, and energy within and between ecosystems and the atmosphere, the ocean, and the Earth.
Surface Deformation and Change: Quantifying models of sea-level and landscape change driven by climate change, hazard forecasts, and disaster impact assessments, including dynamics of earthquakes, volcanoes, landslides, glaciers, groundwater, and Earth’s interior.
NASA is currently initiating the formulation phase for the observatory. Among its first integrated parts is NASA’s partnership with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), which brings together two different kinds of radar systems that can measure changes in Earth’s surface less than a half-inch. This capability will be utilized in one of the observatory’s first missions intended as a pathfinder, called NISAR (NASA-ISRO synthetic aperture radar). This mission will measure some of the planet’s most complex processes such as ice-sheet collapse and natural hazards such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and landslides. NISAR can assist planners and decision makers with managing both hazards and natural resources in the future.
Source: nasa.gov